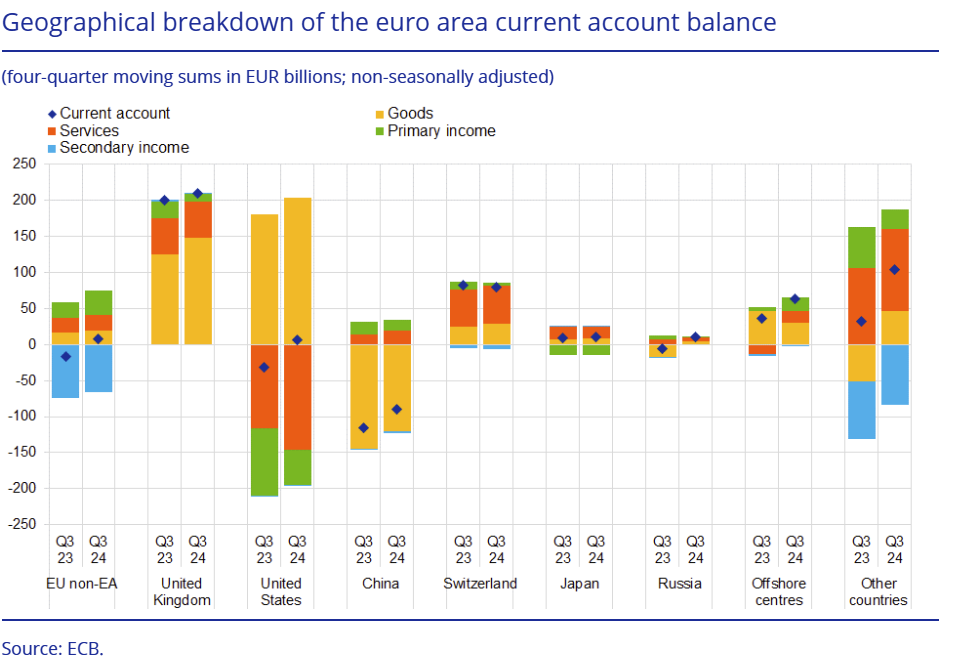
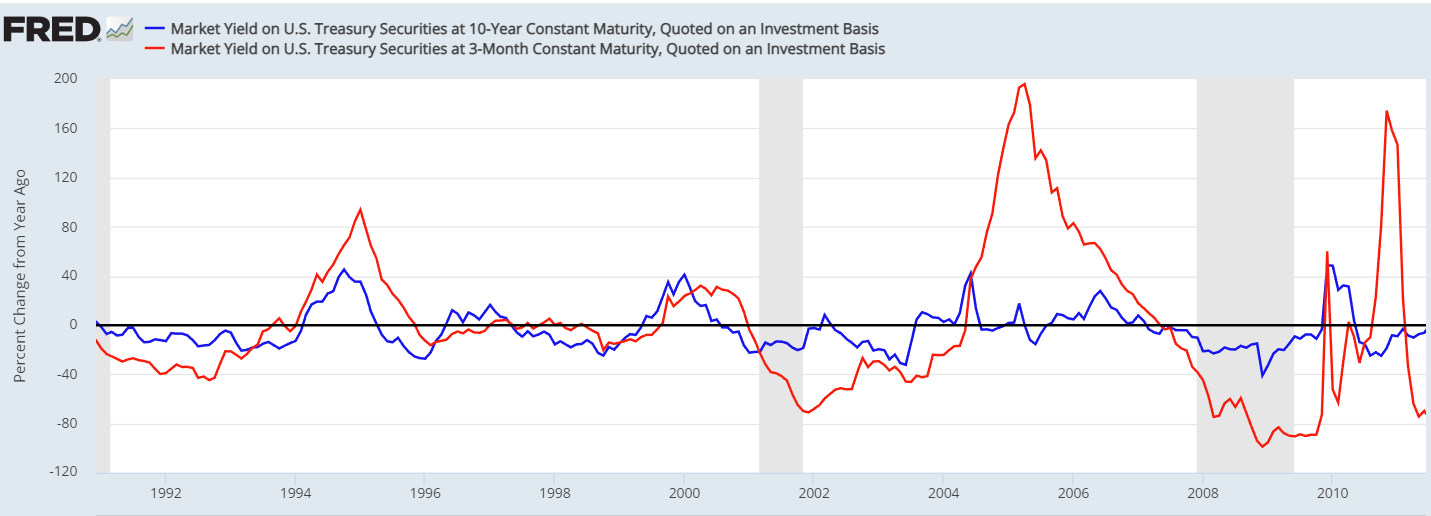
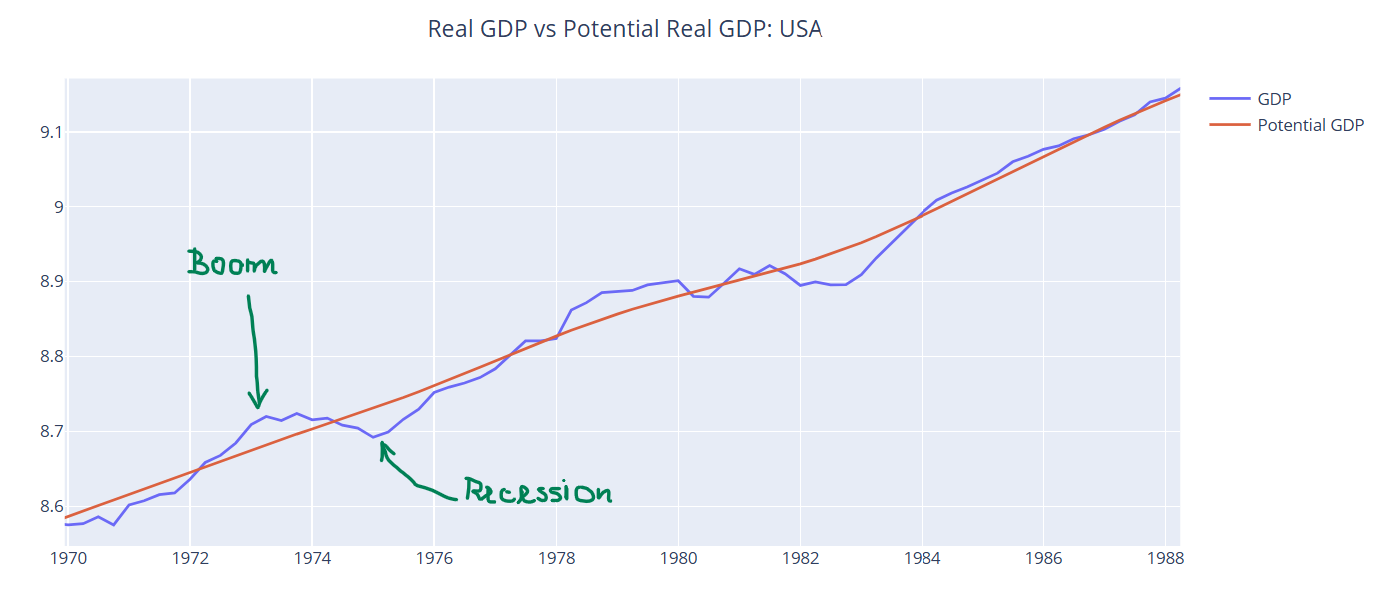
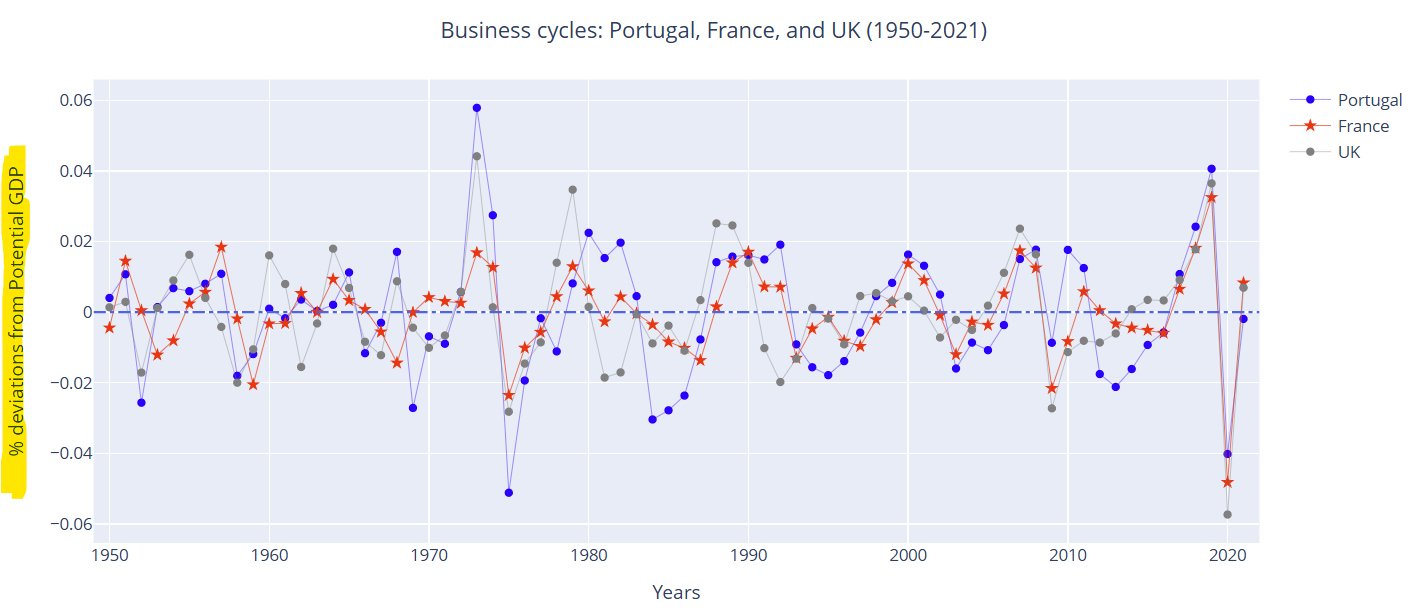
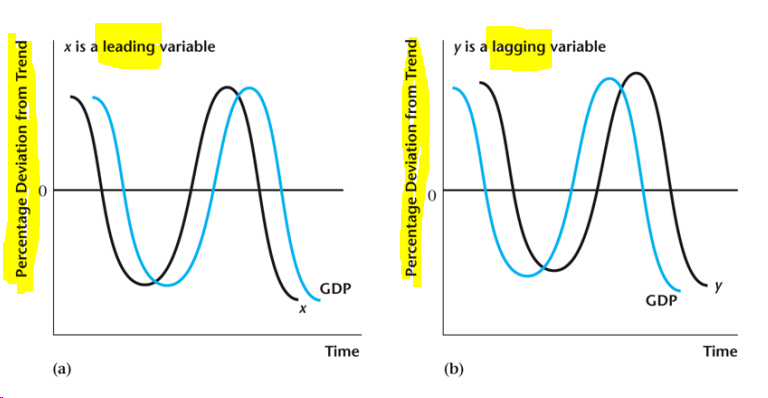
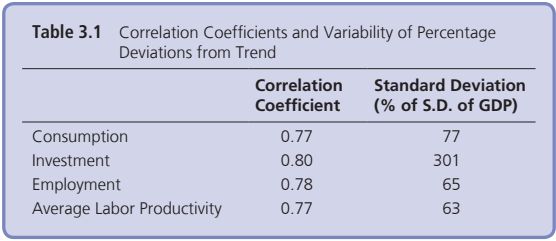
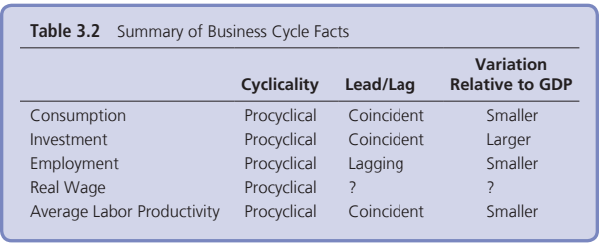
Main Macroeconomic Variables
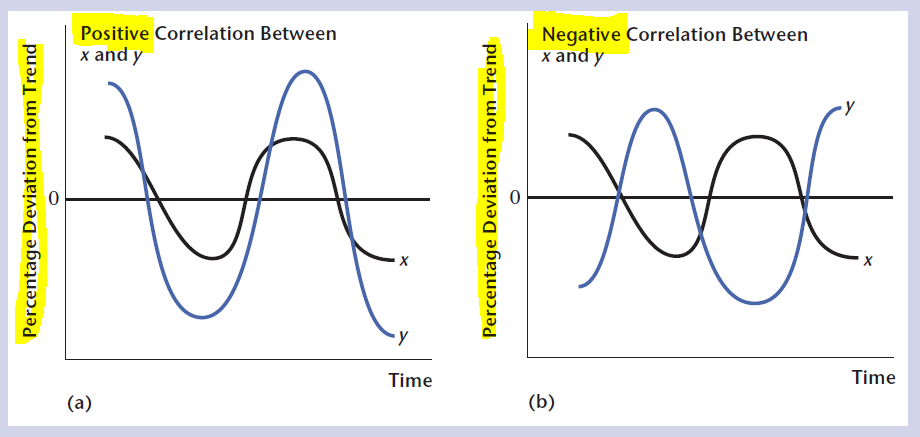
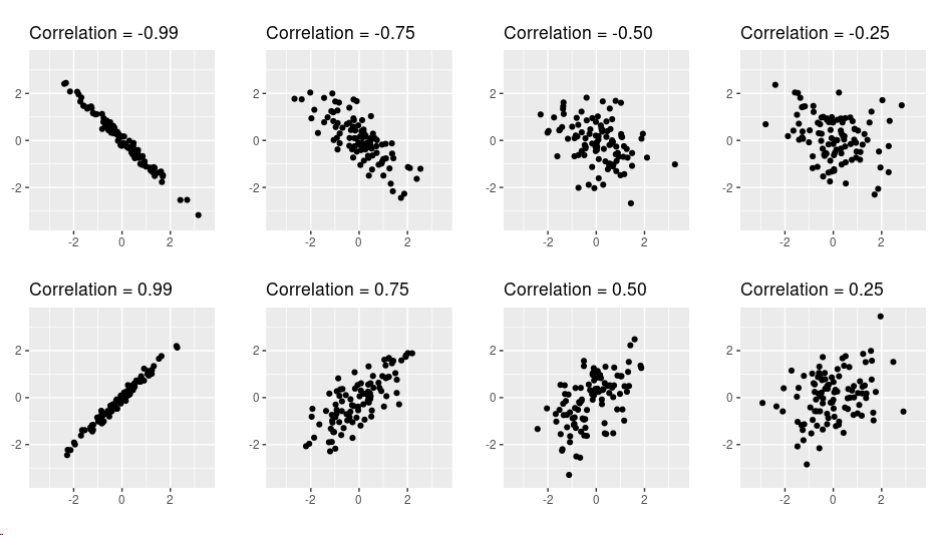
- Real GDP (Gross Domestic Product) and its components
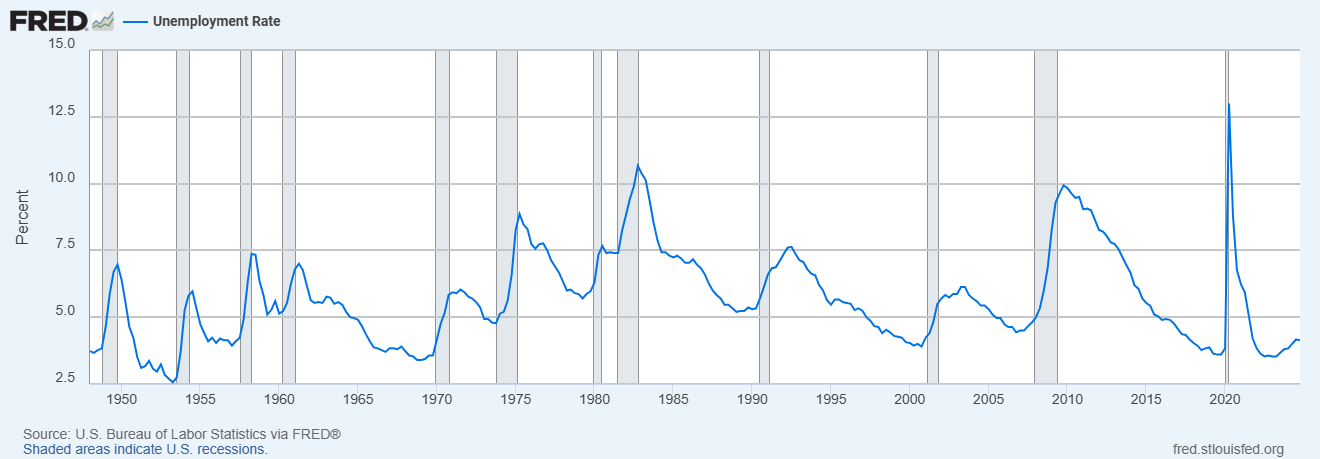
- Unemployment, employment, and participation rates
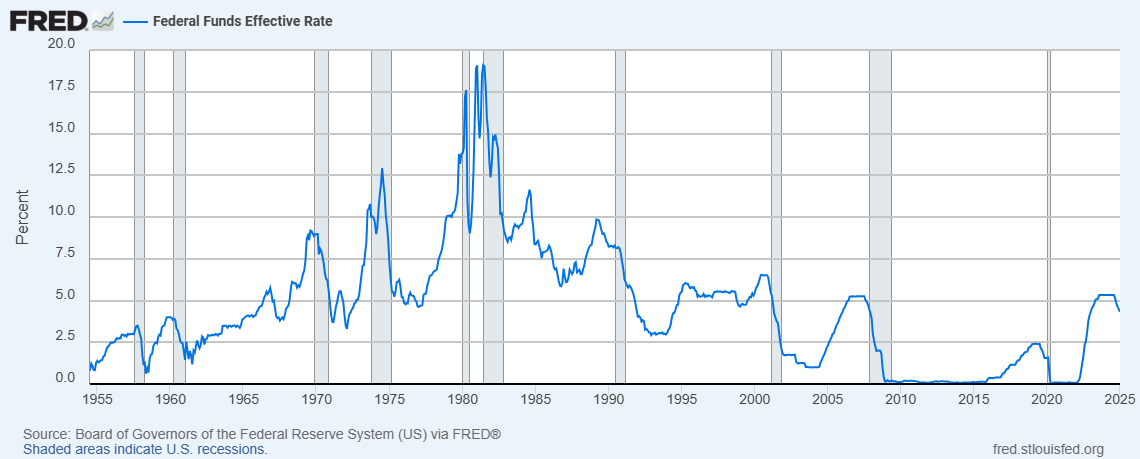
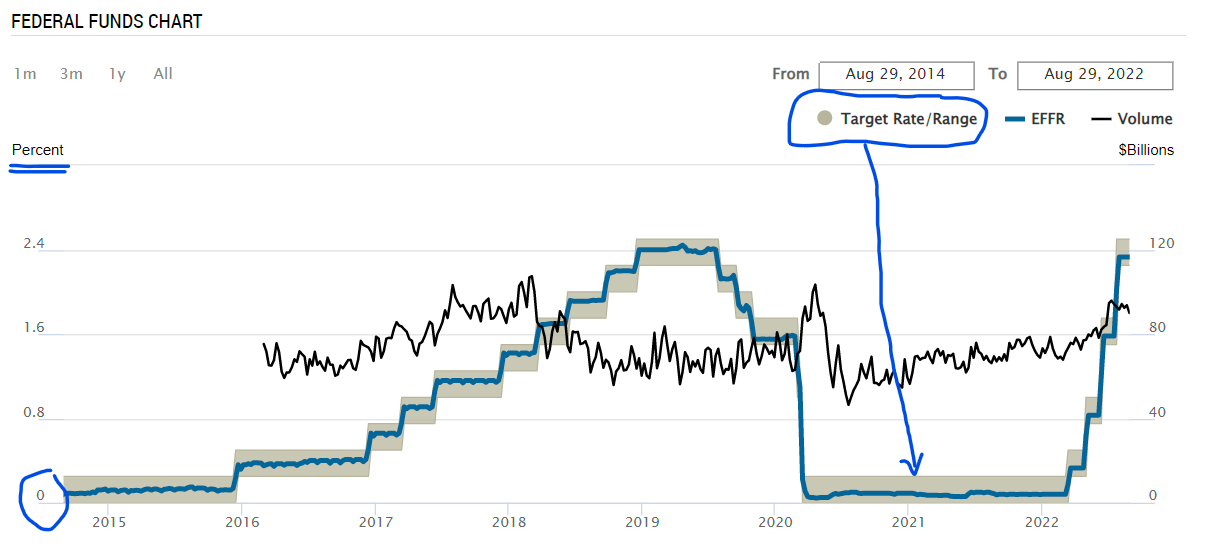
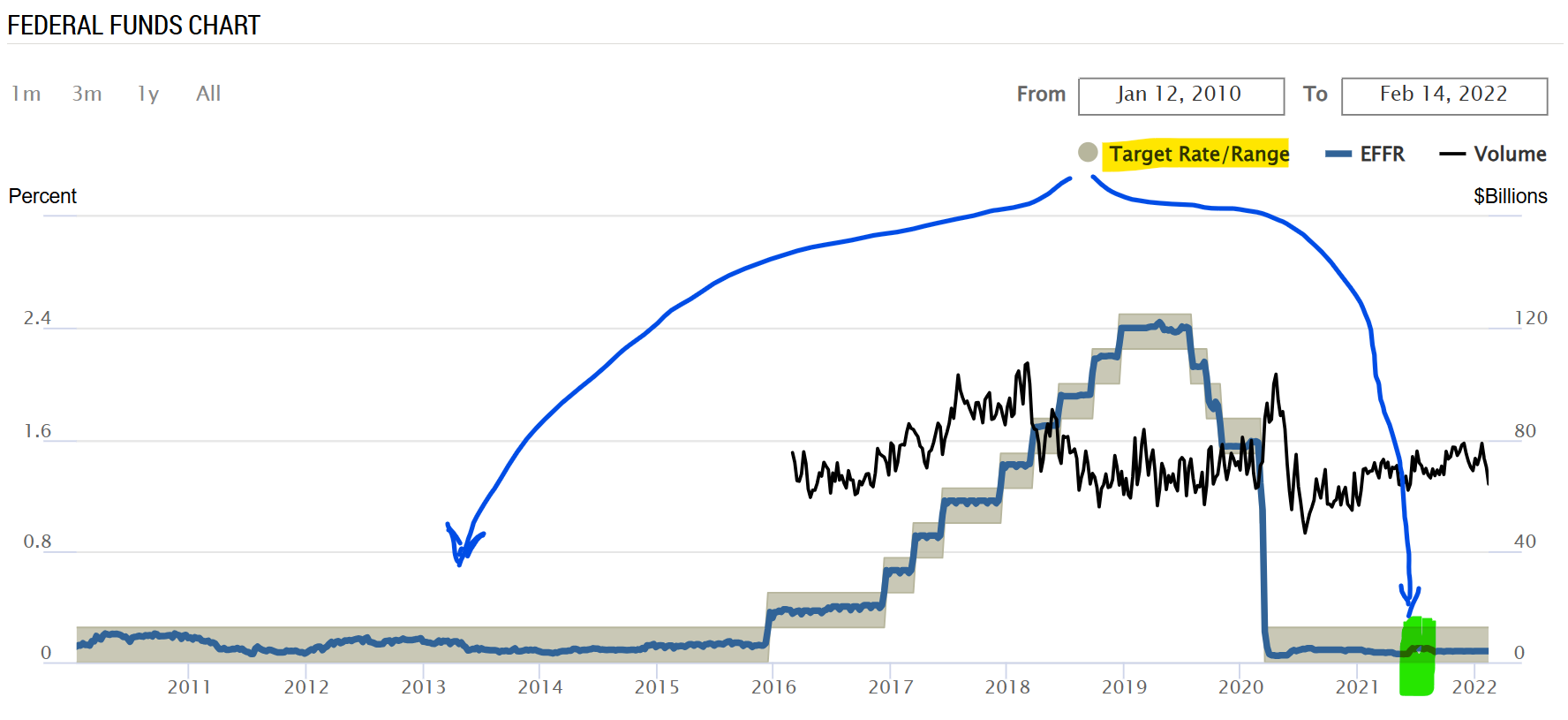
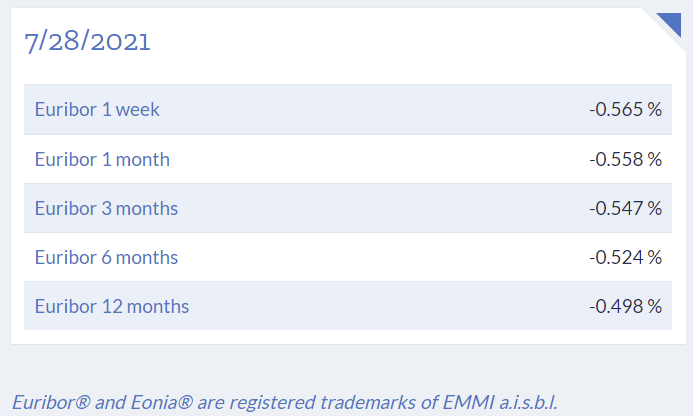
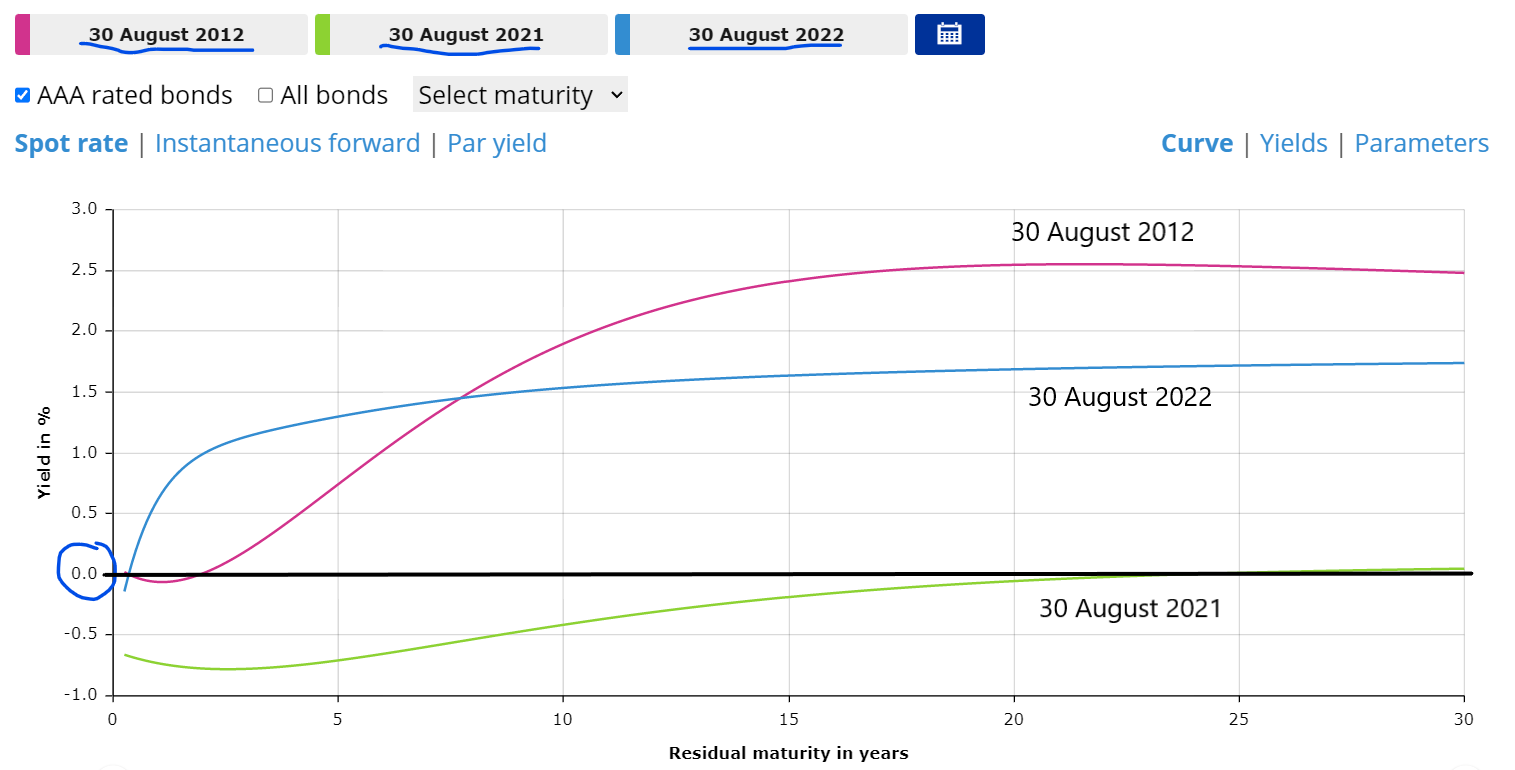
- Inflation rate and interest rates
- Public budgets and public debt
Excellent sources of macroeconomic data:
- For the US economy go here: FRED Economic Data
- For the EU economy go here: EUROSTAT Data
- For World economic data: TED Data